How Play-Based Learning Enhances Cognitive Development in Early Childhood
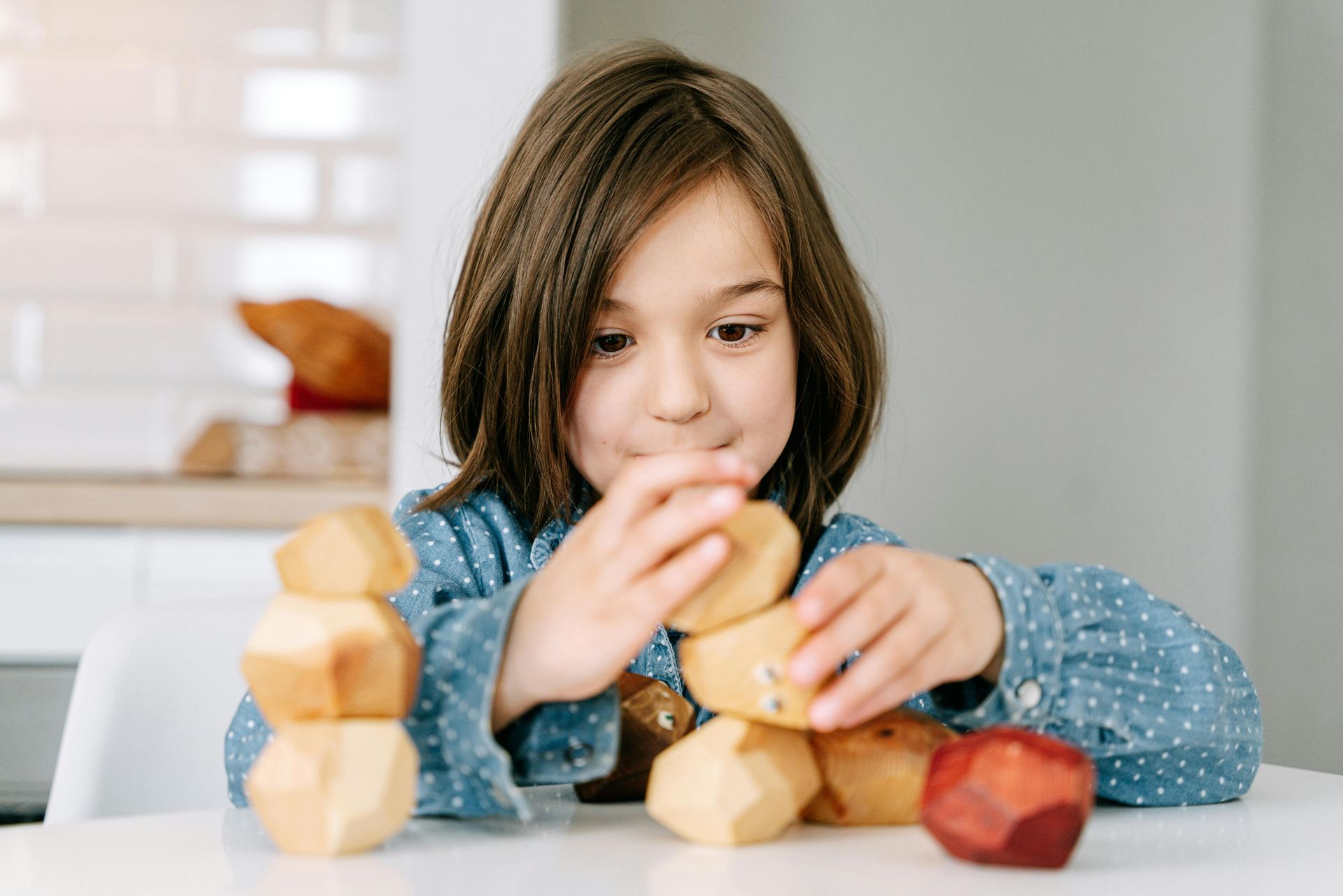

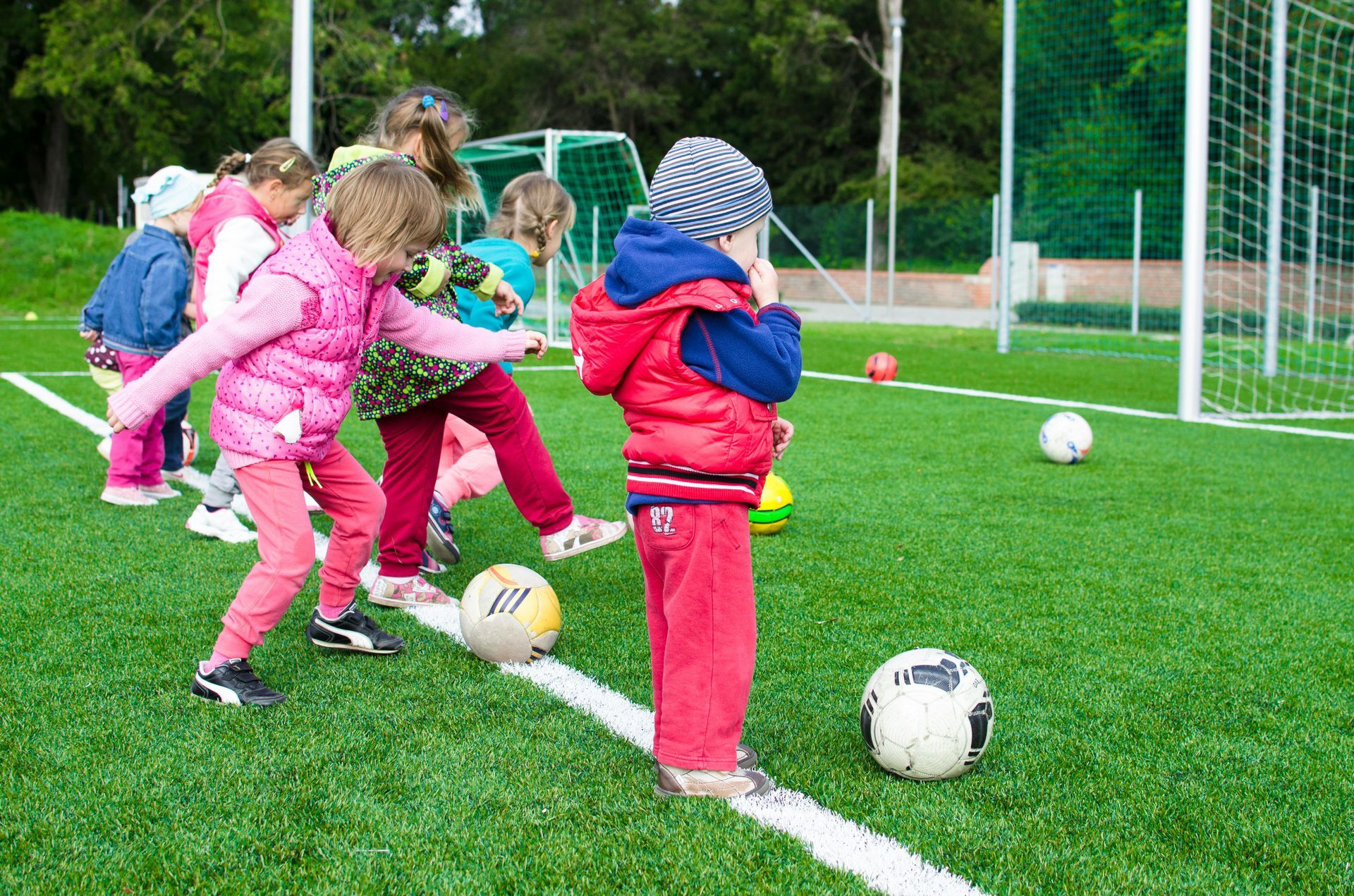
Play is often seen as a break from learning, but in reality, it is one of the most important ways young children learn. At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we understand that play-based learning is not just about having fun—it is an essential strategy that supports cognitive development in early childhood. This approach allows children to explore, problem-solve, and discover the world around them in ways that traditional classroom activities cannot always offer. In this blog post, we’ll delve into how play-based learning fosters cognitive growth and why it’s an integral part of early education.
The Power of Play in Cognitive Development
Cognitive development refers to the mental processes involved in gaining knowledge and understanding, such as thinking, problem-solving, memory, and decision-making. Play-based learning allows children to engage in activities that directly stimulate their cognitive abilities. Through imaginative and interactive play, children develop critical thinking skills, creativity, and an understanding of the world. Let’s take a closer look at how play-based learning enhances cognitive development:
- Encouraging Problem-Solving Skills: Play often presents challenges that children must navigate. Whether they are building a tower with blocks, solving a puzzle, or figuring out how to share a toy, these activities encourage children to think critically and come up with solutions. Each problem they encounter helps them practice problem-solving techniques that are crucial for their intellectual growth.
- Promoting Creativity and Imagination: Play-based learning provides a natural environment for children to explore their creativity. Activities like role-playing, building with various materials, or painting enable children to think outside the box and express themselves in unique ways. This imaginative play helps them develop innovative thinking skills that will serve them throughout their lives.
- Building Language and Communication Skills: Play allows children to engage in rich verbal exchanges with their peers and teachers. They negotiate roles during playtime, describe actions, and ask questions, all of which improve their language skills. The vocabulary they build through play is essential for their cognitive development and academic success. Play also encourages children to listen, interpret, and respond thoughtfully—skills they will need in both academic and social contexts.
- Enhancing Memory and Focus: As children engage in various play activities, they exercise their memory and concentration. Whether it’s remembering the steps of a game, following the rules of a puzzle, or recalling the details of a story they’ve created, play helps improve their ability to retain information. Repeated play activities also help strengthen memory retention, allowing children to better focus and process information in different contexts.
- Supporting Executive Functioning Skills: Executive functioning refers to a set of cognitive skills that enable individuals to plan, organize, and execute tasks. Play-based learning naturally supports the development of these skills as children engage in activities that require planning (such as setting up a game), organizing (arranging objects in a certain way), and following through with their ideas. These skills are critical for academic achievement and later success in life.
The Role of Teachers in Play-Based Learning
While play-based learning is often child-driven, teachers play a vital role in guiding and facilitating the experience. At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, our teachers create an environment where children feel safe to explore, experiment, and learn through play. Here’s how our educators foster cognitive development through play-based learning:
- Providing Purposeful Play Opportunities: Teachers plan play activities that are designed to enhance specific areas of cognitive development. For example, a teacher may set up a building block station to encourage problem-solving and spatial reasoning, or a pretend kitchen to promote social and language skills. By carefully selecting play materials and activities, teachers ensure that children engage in meaningful experiences that challenge their thinking.
- Scaffolding Play: Scaffolding refers to the support teachers provide during play to help children move to the next level of understanding. For example, when a child is building with blocks, the teacher may ask questions that prompt them to think about balance, shapes, and structures. As the child’s skills improve, the teacher gradually reduces their guidance, allowing the child to take on more responsibility and solve problems independently.
- Encouraging Cooperative Play: Play often involves working with others, which helps children develop social and cognitive skills simultaneously. Teachers encourage cooperative play, where children work together to achieve a common goal. Through cooperative activities, children learn to communicate, share, and collaborate—all of which strengthen their cognitive abilities.
- Observing and Documenting Progress: Teachers observe children during play to assess their cognitive development and tailor their teaching strategies accordingly. By documenting children’s actions, conversations, and behaviors during play, teachers can track progress and identify areas where further support may be needed. This allows for more personalized and effective learning experiences.
Examples of Play-Based Learning Activities at Play Laugh and Grow Academy
At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we incorporate play-based learning throughout our curriculum. Here are some examples of activities that help children develop essential cognitive skills:
- Building and Construction Play: Using blocks, Legos, and other materials, children engage in building structures that require planning, problem-solving, and fine motor skills. This type of play supports the development of spatial awareness and logical thinking.
- Pretend Play: Whether it’s playing house, setting up a store, or pretending to be astronauts, pretend play encourages creativity, role-taking, and social interaction. It also strengthens language development as children act out various scenarios and practice new vocabulary.
- Sensory Play: Activities like playing with sand, water, or finger painting allow children to explore textures and engage their senses. Sensory play promotes fine motor skills and cognitive development as children experiment with different materials and discover cause-and-effect relationships.
- Storytelling and Dramatic Play: Storytelling allows children to use their imagination and practice language skills. In dramatic play, children act out stories or create their own, fostering cognitive development through creative expression, sequencing, and narrative thinking.
- Problem-Solving Games: Puzzles, matching games, and memory games encourage children to think critically, recognize patterns, and improve their memory. These games promote cognitive skills such as reasoning and concentration.
The Long-Term Benefits of Play-Based Learning
The benefits of play-based learning extend far beyond the early childhood years. Children who engage in play-based learning are better prepared for formal education, and they develop skills that will serve them throughout their lives. Here are some long-term benefits of play-based learning:
- Enhanced Cognitive Flexibility: Play-based learning fosters cognitive flexibility, allowing children to adapt to new situations, think critically, and approach problems from different angles. This flexibility is essential in school, work, and everyday life.
- Stronger Academic Performance: Research shows that children who engage in play-based learning perform better academically. The problem-solving, creative thinking, and language skills developed during play translate directly into success in formal education settings.
- Improved Social and Emotional Skills: The social interactions involved in play-based learning help children develop emotional intelligence, which is crucial for managing relationships and emotions later in life. These skills promote a positive outlook, resilience, and the ability to navigate complex social situations.
- Increased Confidence and Independence: Play encourages children to take risks, try new things, and solve problems on their own. As children gain confidence in their abilities, they become more independent learners and are better equipped to tackle challenges.
- Lifelong Love of Learning: The joy and excitement that comes from play-based learning can help children develop a lifelong love of learning. Play encourages curiosity, exploration, and self-motivation, which are key to continued success in education and beyond.
Discover the impact of early childhood education on shaping lifelong learning and the importance of social skills in development by reading the blog posts
Building Strong Foundations: How Early Childhood Education Shapes Lifelong Learning and
The Importance of Social Skills in Early Childhood Education.
Conclusion
Play-based learning is a powerful and essential tool for cognitive development in early childhood. At Play Laugh and Grow Academy, we believe in the transformative power of play to foster critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and social-emotional growth. By incorporating play-based learning into our curriculum, we give children the foundation they need to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally. Play is not just a fun activity—it is the gateway to a lifetime of learning and success.